The patient monitor is a diagnostic electronic device which is a monitor which consists of one or further monitoring sensors that help to record the patient’s vital medical signs such as blood pressure, body temperature, SPO2 level, pulse rate,etc....
Therefore these patient monitors known as Multi-Parameter Patient Monitors.
History:

In Italy, it was published the first method of pulse rate measurement and temperature measurement by Mr.Santorio in 1625. And also in 1707, it was published the ‘Pulse Watch’ by Sir John Floyer. In 1852, Mr.Taube plotted the first fever curve. Also in 1896, Mr.Riva Rocci invented the blood pressure cuff. Finally, in 1903, the first ECG measurement was invented by Einthoven.
By 1920, it has been recorded in medical charts all these newly innovated diagnostic measurements for these vital signs of pulse rate, blood pressure, respiratory rate and temperature. Concurrently, development of the Electronic Instrumentation and Transducers have increased the number of monitored physiological variables.
This machine was used in mostly in ICU’s from the time of the 1950s that was created the ICU concept. Initially, as post-operative recovery rooms, and in the 1960s came more variations including Coronary Care Units which monitored the cardiac rhythmicity.
Therefore in 1966, took computers to the ICU by Mr.Shubin and Mr.Weil in Los Angeles for computing the derived variables which cannot be directly measured also for increasing patient care efficacy.
How this Machine Works:
This patient monitor consists of a built-in charge battery and it started to charge at the time of the power cable is connected to the AC power supply. Therefore check the AC power cable that has been plugged properly to the AC power supply. Then Switch on the patient monitor and verify the display/screen of the monitor and the vital parameters are displaying on the screen properly.
And check all the accessories are connected/linked to the monitor properly and cleaned (Should all ways keep the machine in the dust-free environment and provide all the necessary room temperature according to the manufacturer’s guidelines).
Then connect all the Temperature transducer, NIBP Cuff, Saturation probe, ECG leads to the patient properly. Be aware that the patient is not talking or not doing any other activities before going to measure and diagnose each and every parameter.
Working Theory/Principle:
The patient monitor consists of the main unit and subsequent the other functional components such as the ECG electrodes and leads, NIBP(non-invasive blood pressure cuff), temperature transducer, SpO2 probe and also as optional IBP( invasive blood pressure) and side-stream CO2.
The following figure shows the overall working structure of the patient monitor medical device.
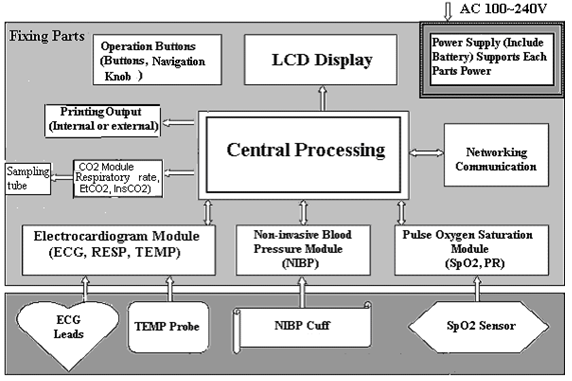 |
| The basic structure of the patient monitor. |
These different modules perform different physiological parameter measurements. And this module design includes six modules as, NIPB module, ECG module, SpO2 module, as optional IBP module and CO2 modules can be taken into account.
The followings have been explained each and every module's function:
1. NIBP Module – It is collecting data of blood pressure, including systolic, diastolic and also the mean arterial pressure throughout the (NIBP) cuff. These cuffs are available in different sizes for adults, infants and neonates. And there are two modes on the patient monitor of NIBP measurements and one mode for adults, infants and the other mode for neonates.
2. ECG Module – It is collecting the respiration waveforms, heart rate, through the ECG electrodes & leads.
3. SpO2 Module - The SpO2 module collects the data of pulse rate, pulse oxygen saturation (SpO2) and SpO2 volume waveform via the SpO2 probe.
4. CO2 Module – This CO2 module is collecting EtCO2, InsCO2 and the date of respiration rate through the sampling tube.
5. The Main Unit – This unit consists of the mainboard, keyboard, and the multi-function board. This multi-function board act upon the data communication among the ECG module, NIBP module, SpO2 module, CO2 module and the main module.
Uses/Benefits of Patient Monitors:
The patient monitor delivers high-quality care and lower risk. What does this device do is diagnosing, monitoring and recording the patient’s vital signs. Then it helps to identify the ailments and reduce the risks of a life at the early stage of the patient.
(i) To Maintain Diabetes:
In order to control diabetes, it should take care of the blood pressure, weight, blood glucose etc. For this, these diagnostic and monitoring devices assist the real-time delivery of blood glucose level and blood pressure helps or alert to the healthcare provider for treating when needed.
(ii) To Reduce the Risk of Heart Failure:
Due to the frenzied lifestyle, there are lots of people in the public community are suffering from different types of heart failures. Therefore to reduce the risk of these heart failure, there are devices such as pacemakers, cardiac resynchronization that brought by the technology in the market. This improves the quality of life and also helps to decrease the mortality rate and also the shortens of the duration of staying in the hospitals.
(iii) To Prevent Dementia and Falls:
When people are getting old, their sensory is impairment. Therefore people are at risk of having dementia and falls. In order to prevent these kinds of risks, and therefore this monitoring technology helps to prevent harm & promoting safety via continuous surveillance. There are different types of sensors that are attached to mobility devices. They are such as canes and walkers of the patient that alert of falling.
(iv) To Provide the Condition of the Patient to the Physician in Real-Time:
By checking the main screen of the monitor, the physician is able to understand the present condition of the patient in vital signs and start giving medication in real-time.
(v) To Monitor, the Patient’s Health Condition All the Time:
Therefore it would be easy to diagnose whether the patient is having a chronic disease or heart failure. This early diagnoses will help the patient to extend his/ her life
Accessories of the Patient Monitor:
There are many accessories for this device. Those are as follows considering the accessories sets for one patient monitor:-
(1) One set of ECG lead cable:
1. NIBP Module – It is collecting data of blood pressure, including systolic, diastolic and also the mean arterial pressure throughout the (NIBP) cuff. These cuffs are available in different sizes for adults, infants and neonates. And there are two modes on the patient monitor of NIBP measurements and one mode for adults, infants and the other mode for neonates.
2. ECG Module – It is collecting the respiration waveforms, heart rate, through the ECG electrodes & leads.
3. SpO2 Module - The SpO2 module collects the data of pulse rate, pulse oxygen saturation (SpO2) and SpO2 volume waveform via the SpO2 probe.
4. CO2 Module – This CO2 module is collecting EtCO2, InsCO2 and the date of respiration rate through the sampling tube.
5. The Main Unit – This unit consists of the mainboard, keyboard, and the multi-function board. This multi-function board act upon the data communication among the ECG module, NIBP module, SpO2 module, CO2 module and the main module.
Uses/Benefits of Patient Monitors:
The patient monitor delivers high-quality care and lower risk. What does this device do is diagnosing, monitoring and recording the patient’s vital signs. Then it helps to identify the ailments and reduce the risks of a life at the early stage of the patient.
(i) To Maintain Diabetes:
In order to control diabetes, it should take care of the blood pressure, weight, blood glucose etc. For this, these diagnostic and monitoring devices assist the real-time delivery of blood glucose level and blood pressure helps or alert to the healthcare provider for treating when needed.
(ii) To Reduce the Risk of Heart Failure:
Due to the frenzied lifestyle, there are lots of people in the public community are suffering from different types of heart failures. Therefore to reduce the risk of these heart failure, there are devices such as pacemakers, cardiac resynchronization that brought by the technology in the market. This improves the quality of life and also helps to decrease the mortality rate and also the shortens of the duration of staying in the hospitals.
(iii) To Prevent Dementia and Falls:
When people are getting old, their sensory is impairment. Therefore people are at risk of having dementia and falls. In order to prevent these kinds of risks, and therefore this monitoring technology helps to prevent harm & promoting safety via continuous surveillance. There are different types of sensors that are attached to mobility devices. They are such as canes and walkers of the patient that alert of falling.
(iv) To Provide the Condition of the Patient to the Physician in Real-Time:
By checking the main screen of the monitor, the physician is able to understand the present condition of the patient in vital signs and start giving medication in real-time.
(v) To Monitor, the Patient’s Health Condition All the Time:
Therefore it would be easy to diagnose whether the patient is having a chronic disease or heart failure. This early diagnoses will help the patient to extend his/ her life
Accessories of the Patient Monitor:
There are many accessories for this device. Those are as follows considering the accessories sets for one patient monitor:-
(1) One set of ECG lead cable:
(2) One set of NIBP cuff including for adults, paediatrics and infants:
(3) One piece of SpO2 probe including for adults and paediatrics:
(4) One piece of Body temperature probe:
(5) One piece of the Power supply cable:
(6) Ten pieces of Disposable electrodes:
(7) Printing paper rolls:
(8) CO2 probe (optional):
Types of Patient Monitors:
There are different types of patient monitors depend on the unit of the hospital. The patient monitor has been made out of different parameters depend on the necessity vital parameters to be checked/diagnosed of the particular unit of the hospital can choose the type of the patient monitor.
Therefore depend on the classification of the target parameter, there are types of monitoring as follows:
(1) Cardiac monitoring
(2) Respiratory monitoring
(3) Hemodynamic monitoring
(4) Neurological monitoring
(5) Blood glucose monitoring
(6) Body temperature monitoring
(7) Childbirth monitoring
(8) Cancer therapy monitoring
Therefore considering the compulsory parameters including the specific type of patient monitor can be used in the different units in the hospital.
Why Do We Need Patient Monitors:
Patient monitors are using to diagnose the early stages of life-threatening diseases such as heart failures etc... and reduce the risk of life-threatening for the patients. Considering the benefits of using this for both sides of patients and the doctors as follows:
For Patients :
• Well-timed & correct treatment at a premature stage.
• Reduced the wait time and travel.
• Several doctors are able to assess the condition from the inaccessible locations when using remote patient monitors.
• Immediacy to the community.
• Able to diagnose rapidly and fast involvement by the doctor.
For Doctors :
• Real-time revelation of medical parameters and patient health.
• Enhance operational efficiency, compliance & planning.
• Live streaming of patient data even in 2G network.
• Reduce workload and clinical productivity.
• Save the time & Resources.
Places Where These Devices are Used in the Hospital:
This patient monitor is using mostly in the Critical Care Unit (CCU) or Intensive Care Unit (ICU), Emergency Treatment Unit (ETU), Intensive Therapy Unit (ITU), Operations Theatres (OT), and sometimes for critical patients of medical and surgical wards.
The Appearance of the Patient Monitor:
Here can be considered the panel sections of the device as follows:
(1) Front Panel:
Here is the front panel of the device and can be seen some buttons on the bottom which can be switched.
Standard Measurements:
Here has been mentioned the normal ranges of each and every parameter of the patient monitor.
1. Ambient Temperature Range: 5℃~40℃
Relative humidity: 30%~80%
Atmospheric pressure: 70kPa~106kPa
Power supply: 100~240VAC
Power frequency: 50/60Hz
2. This apparatus must protect from direct sunlight, to prevent the high temperature inside of it.
3. Should not use in a toxic or inflammable gas environment.
4. Should be kept on a stand to prevent any possible shock.
5. Should not use with the combination in any other equipment that manufacturer has not been instructed.
6. When using this device with (ESU) electrosurgical unit, the operator (doctor or nurse) should pay attention to the safety of the patient.
7. Make sure the equipotential grounding terminal has grounded correctly.
8. Should not use the mobile phone nearby to avoid the strong radiant field interference.
Alarm Information:
(3) One piece of SpO2 probe including for adults and paediatrics:
(4) One piece of Body temperature probe:
(5) One piece of the Power supply cable:
(6) Ten pieces of Disposable electrodes:
(7) Printing paper rolls:
(8) CO2 probe (optional):
Types of Patient Monitors:
There are different types of patient monitors depend on the unit of the hospital. The patient monitor has been made out of different parameters depend on the necessity vital parameters to be checked/diagnosed of the particular unit of the hospital can choose the type of the patient monitor.
Therefore depend on the classification of the target parameter, there are types of monitoring as follows:
(1) Cardiac monitoring
(2) Respiratory monitoring
(3) Hemodynamic monitoring
(4) Neurological monitoring
(5) Blood glucose monitoring
(6) Body temperature monitoring
(7) Childbirth monitoring
(8) Cancer therapy monitoring
Therefore considering the compulsory parameters including the specific type of patient monitor can be used in the different units in the hospital.
Why Do We Need Patient Monitors:
Patient monitors are using to diagnose the early stages of life-threatening diseases such as heart failures etc... and reduce the risk of life-threatening for the patients. Considering the benefits of using this for both sides of patients and the doctors as follows:
For Patients :
• Well-timed & correct treatment at a premature stage.
• Reduced the wait time and travel.
• Several doctors are able to assess the condition from the inaccessible locations when using remote patient monitors.
• Immediacy to the community.
• Able to diagnose rapidly and fast involvement by the doctor.
For Doctors :
• Real-time revelation of medical parameters and patient health.
• Enhance operational efficiency, compliance & planning.
• Live streaming of patient data even in 2G network.
• Reduce workload and clinical productivity.
• Save the time & Resources.
Places Where These Devices are Used in the Hospital:
This patient monitor is using mostly in the Critical Care Unit (CCU) or Intensive Care Unit (ICU), Emergency Treatment Unit (ETU), Intensive Therapy Unit (ITU), Operations Theatres (OT), and sometimes for critical patients of medical and surgical wards.
The Appearance of the Patient Monitor:
Here can be considered the panel sections of the device as follows:
(1) Front Panel:
Here is the front panel of the device and can be seen some buttons on the bottom which can be switched.
 |
| The front panel of the patient monitor. |
1. Power button.
2. AC power indicator.
3. DC power indicator of in-built battery
4. ECG lead selection for shifting the ECG monitoring circulatory among the leads ofⅠ, Ⅱ, and Ⅲ AVL, AVF and V.
5. Alarm silence for 2 min, 5 min, 10 min and 20 min.
6. Freeze for analyze the ECG waveform segments for analyzing according to the system setting.
7. NIBP button to start or stop the NIBP measuring.
8. Print button to print out the ECG wave form.
(2) Rear Panel:
In this rear panel, the main port is the AC power supply socket. Instead of these ports, can be seen the following detailed nameplate of the device.
 |
| Nameplate of the patient monitor |
1 – CE mark
2 – Serial number
3 – Date of manufacturer
4 - Authorized representative in the European community
5 - Manufacturer (including address)
6 - Disposal of this device according to WEEE regulations
(3) Left and right panel:
 |
| Left and right panel |
In this figure from left to right shows in order as left panel and the right panel. The left panel consists of a built-in printer. In the right panel consists of the cable and the probe ports such as:-
1. TEMP probe connector
2. NIBP hose connector
3. SpO2 probe connector
4. ECG cable connector
5. The cable connector of CO2 sensor module
6. Cover of the battery compartment
Components of the Patient Monitor:
There are components as follows:-
1. Sensors – Biosensors such as to measure temperature, SPO2, EtCO2, etc and mechanical sensors are using here.
2. Analog to Digital converter – Converting all the physiological biosignals into a readable digital format which can display on the monitor screen.
3. Display / Output – The screen may be CRT, LED, or LCD. These display devices mostly used digital signal processing (DSP) and are able to track the different vital signs at the same time. This DSP has portability and miniaturization as advantages.
Block Diagram of the Patient Monitor:
The following figure shows the block diagram of the patient monitor. According to that the Physiological signals / the biosignals are coming from the patient of different parameters are detected by the specific transducers. These transducers then convert the physiological signal into an electrical signal which is amplified then and accustomed.
Then that signal passes through to the analogue to digital converter (ADC). Then this converter is sending the data to a microprocessor which is a based signal processor that extracts features such as blood pressure and heart rate.
After processing all these signals are displayed on a display/output device to monitor the condition of the patient.
 |
| Block diagram of the patient monitor. |
Here has been mentioned the normal ranges of each and every parameter of the patient monitor.
 |
| The main screen of the patient monitor |
This above figure shows the main screen of the patient monitor and it clearly declares the normal range measurements of each and every parameter. And it’s described more as follows:-
1. ECG
—Heart Rate or Pulse Rate(①unit:bpm)
—pacer detection (PACE②)
—ST-segment of channel 1 and channel 2 (③unit: mv)
— PVCs times (④ Unit: times/minute)
2. SpO2
—SpO2(⑤ unit:%)
—Pulse Rate(unit:bpm)
3. IBP (optional)
— Invasive Blood Pressure
(From left to right) Systolic, Diastolic, Mean (⑥Unit: mmHg or KPa)
4. NIBP
— None-Invasive Blood Pressure
(From left to right) Systolic, Diastolic, Mean (⑦Unit: mmHg or KPa)
5.RESP
—Respiration Rate(⑧unit:bpm)
6.TEMP
—Temperature(⑨unit: or℃℉)
7.CO2 (optional)
—end-tidal CO2 (⑩ Unit: mmHg or KPa)
—inspiratory CO2 ((11) Unit: mmHg or KPa)
—Air-Way Respiration Rate (AWRR),unit:bpm)
Operating Environment of the Patient Monitor:
The following environment should provide to the patient monitor to be functioned well:-
1. Ambient Temperature Range: 5℃~40℃
Relative humidity: 30%~80%
Atmospheric pressure: 70kPa~106kPa
Power supply: 100~240VAC
Power frequency: 50/60Hz
2. This apparatus must protect from direct sunlight, to prevent the high temperature inside of it.
3. Should not use in a toxic or inflammable gas environment.
4. Should be kept on a stand to prevent any possible shock.
5. Should not use with the combination in any other equipment that manufacturer has not been instructed.
6. When using this device with (ESU) electrosurgical unit, the operator (doctor or nurse) should pay attention to the safety of the patient.
7. Make sure the equipotential grounding terminal has grounded correctly.
8. Should not use the mobile phone nearby to avoid the strong radiant field interference.
Alarm Information:
 |
| Information about the Alarm system of the Patient monitor |
Working Principle of the Parameters of the Patient Monitor:
1. Measuring principle of the NIBP monitoring:-
In here the blood pressure of the patient is measured in a non-invasive way. This non-invasive way also includes different methodologies such as oscillating method and the ‘knockoff’ sound method that determines the systolic and diastolic blood pressure that detects the arterial sound using a stethoscope. This is applied to the brachial artery distal to the blood pressure cuff of the sphygmomanometer that is changing with cuff pressure.
Here using the oscillating method that the air will be filled by an inflation pump and release it slowly. Then the computer will record the change of the cuff pressure. Then the blood pressure value will be determined with this record.
2. Measuring principle of the SPO2 monitoring:-
For this monitoring, the method uses is the ‘Lamber-Beer’ law that is the absorption of the light of a given material. This is directly proportional to the concentration or its density. There is a different absorption range for oxygenated and deoxygenated haemoglobin (HbO2 and Hb) of the blood.
Therefore SpO2 measured by this patient monitor is the functional oxygen saturation as a percentage of haemoglobin that can be transported by oxygen.
3. Measuring principle of the respiration monitoring:-
Chest volume of the human lungs changes due to the volume of air filling inside to that when inhaling and releasing the air when exhaling. The conductivity of the body tissues are higher than the air. Therefore due to this inflation, the chest impedance will be changed.
Thus with this specialization respiration can be measured by sending a high frequency than the ECG, through the ECG electrodes to be measured the ECG signal as well as the chest impedance at the same time. Finally, it will be able to measure the respiratory rate according to an impedance method by using the software.
4. Measuring principle of temperature monitoring:-
It is using a sensor of thermo-resistor type (25℃, 5kΩ) which has supplied with a constant microcurrent. This temperature monitoring can be done in two different measuring methods such as measuring the body surface temperature and also through the temperature inside the body cavity (placed in anus or mouth).
5. Measuring principle of the CO2 monitoring:-
Here uses an IR beam and it is passed through a breathing gas sample and it is detected by a photodetector. Then this IR beam energy is absorbed by CO2 of this gas sample. Therefore the absorbed energy is directly proportional to the CO2 concentration of the gas sample.
Then to get the final output can be calibrated with a known value of CO2 concentration that is stored in the monitor’s memory according to the response of the photodetector. Finally, it displays as a numerical value in millimetres of mercury (mmHg) as a percentage (%), or kilopascals (kPa).
Troubleshooting:
There are some failures or troubles which may occur. Therefore following instructions can be followed to eliminate the problem:-
1. If the screen is not displayed -
• Shut down and unplug the AC power cable of the machine and check whether there is showing the proper voltage and check the continuity of the fuse using a universal meter.
• And also check the power cable wire and the socket, to check if there is any damage occurred and whether it is properly connected to the device.
2. If shows the external interferences of the ECG waveform on the monitor screen ;
• Check the ECG lead wires are broken or connected properly to the monitor.
• Check the ground wire of the monitor is properly grounded.
• Check the electrodes whether valid is using which connecting to the patient.
3. Not showing the NIBP range and the oxygen saturation of the monitor screen ;
• Make sure the blood pressure cuff has a leakage and it has been properly wrapped on the patient’s arm.
• Make sure that the patient is not talking or not engaging with any other work during getting the measurements of the blood pressure.
• Check the SPO2 probe is properly connected to the patient and the monitor
• Check whether the bulb is not blinking of the SPO2 probe when it’s connected to the patient.
• Still the problem is remaining contact the manufacturer.
4. The alarm system is not working properly ;
• Check whether the alarm limit value is proper for the condition of the patient.
• Check the probe connections.
• Check the lead connection.
Maintenance of the Patient Monitor:
There are some maintenance tips that can be carried out:
- Checking the monitor to verify whether there is any mechanical damage.
- Inspecting the exposed parts, inserted parts of all leads, and the accessories of the device.
- Examining all functions of the monitor of all parameters which is used for patient monitoring at the time, and make sure that all is in good working condition.
- Make sure that the earth wire of the monitor is grounded properly.
- Pay close attention to the fluctuation of the local power supply voltage.
References:
- Annicchiarico R, Cortés U, Urdiales C. Switzerland: Birkhäuser Verlag; 2008. Agent Technology and e-Health
- Blumenthal D. Stimulating the Adoption of Health Information Technology. N Engl J Med. 2009
- Cresswell K, Sheikh A. Organizational issues in the implementation and adoption of health information technology innovations: An interpretative review. International journal of medical informatics. 2013
- Isern D, Sánchez D, Moreno A. Agents applied in health care: A review. International journal of medical informatics. 2010
- Mohammadzadeh M, Safdari R, Rahimi A. Multi-Agent System as a New Approach to Effective Chronic Heart Failure Management: Key Considerations. Healthc Inform Res. 2013 Sep;19
- Paré G, Moqadem K, Pineau G, St-Hilaire C. Clinical Effects of Home Tele monitoring in the Context of Diabetes, Asthma, Heart Failure and Hypertension: A Systematic Review. J Med Internet Res. 2010













Very informative. Thank you very much!
ReplyDeleteThank you!
DeleteWhen social media is misunderstood or misapplied, it can turn into a time sink where many hours that could have been spent more productively in other ways to build your business. rallys low carb
ReplyDelete