Dear Healthcare Professionals, 👩⚕️👨⚕️👩🔬👨🔬
👩🎓👩💻 Since our Articles get very good impressions and high appreciations from our Blog's visitors from all around the globe; we would like to invite you to publish your articles with us on our website 👉( https://learnbiomedengine.blogspot.com/) along with your profiles! 👨🎓👨💻
👉 We assure you that this will make yourself and your articles very popular and highlighted throughout the entire healthcare sector which is an added advantage to you in future! 👍
👉 Please email to sam.gastondiaz@gmail.com for getting more details! 👍

We are one of the best Modern Medical Technology Consultation Service Providers in Asia. This blog is a free resource we offer for the public to access knowledgeable materials from us. If you are a Healthcare Professional or Someone who has a passion for building up the Healthcare Sector through Advanced Technology to Provide Better Healthcare Facilities, you are at the right place. Please join hands with us, to make a better world through Advanced Healthcare Technology.
Sunday, April 26, 2020
Show Your Healthcare Related Articles to the World !!!
Hi,
👩💻 Are you interested in writing Articles? 👨💻
👩🎓 Do you like to present your Articles to the world and get recognitions for your Articles and for your Skills? 👨🎓
👩🔬 Would you like to get Good Impressions to your Profile? 👨🔬
👉 We can support you by giving a space for your amazing Articles with our renowned, high traffic Healthcare website! 👈 (https://learnbiomedengine.blogspot.com/)👍
👉 If you’re interested please send an email to sam.gastondiaz@gmail.com for requesting more details… 👈 👍
👩💻 Are you interested in writing Articles? 👨💻
👩🎓 Do you like to present your Articles to the world and get recognitions for your Articles and for your Skills? 👨🎓
👩🔬 Would you like to get Good Impressions to your Profile? 👨🔬
👉 We can support you by giving a space for your amazing Articles with our renowned, high traffic Healthcare website! 👈 (https://learnbiomedengine.blogspot.com/)👍
👉 If you’re interested please send an email to sam.gastondiaz@gmail.com for requesting more details… 👈 👍
Wednesday, April 15, 2020
Patient Monitor.
Overview:
History:

These different modules perform different physiological parameter measurements. And this module design includes six modules as, NIPB module, ECG module, SpO2 module, as optional IBP module and CO2 modules can be taken into account.
The patient monitor is a diagnostic electronic device which is a monitor which consists of one or further monitoring sensors that help to record the patient’s vital medical signs such as blood pressure, body temperature, SPO2 level, pulse rate,etc....
Therefore these patient monitors known as Multi-Parameter Patient Monitors.
History:

In Italy, it was published the first method of pulse rate measurement and temperature measurement by Mr.Santorio in 1625. And also in 1707, it was published the ‘Pulse Watch’ by Sir John Floyer. In 1852, Mr.Taube plotted the first fever curve. Also in 1896, Mr.Riva Rocci invented the blood pressure cuff. Finally, in 1903, the first ECG measurement was invented by Einthoven.
By 1920, it has been recorded in medical charts all these newly innovated diagnostic measurements for these vital signs of pulse rate, blood pressure, respiratory rate and temperature. Concurrently, development of the Electronic Instrumentation and Transducers have increased the number of monitored physiological variables.
This machine was used in mostly in ICU’s from the time of the 1950s that was created the ICU concept. Initially, as post-operative recovery rooms, and in the 1960s came more variations including Coronary Care Units which monitored the cardiac rhythmicity.
Therefore in 1966, took computers to the ICU by Mr.Shubin and Mr.Weil in Los Angeles for computing the derived variables which cannot be directly measured also for increasing patient care efficacy.
How this Machine Works:
This patient monitor consists of a built-in charge battery and it started to charge at the time of the power cable is connected to the AC power supply. Therefore check the AC power cable that has been plugged properly to the AC power supply. Then Switch on the patient monitor and verify the display/screen of the monitor and the vital parameters are displaying on the screen properly.
And check all the accessories are connected/linked to the monitor properly and cleaned (Should all ways keep the machine in the dust-free environment and provide all the necessary room temperature according to the manufacturer’s guidelines).
Then connect all the Temperature transducer, NIBP Cuff, Saturation probe, ECG leads to the patient properly. Be aware that the patient is not talking or not doing any other activities before going to measure and diagnose each and every parameter.
Working Theory/Principle:
The patient monitor consists of the main unit and subsequent the other functional components such as the ECG electrodes and leads, NIBP(non-invasive blood pressure cuff), temperature transducer, SpO2 probe and also as optional IBP( invasive blood pressure) and side-stream CO2.
The following figure shows the overall working structure of the patient monitor medical device.
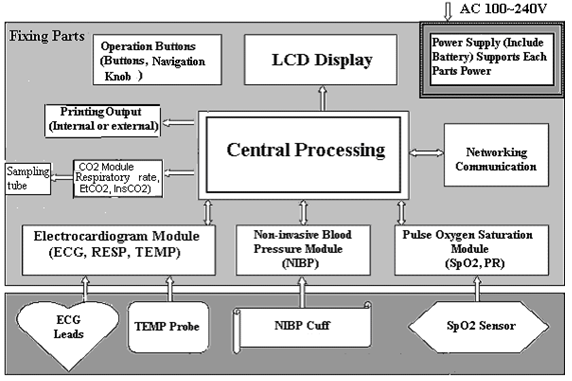 |
| The basic structure of the patient monitor. |
These different modules perform different physiological parameter measurements. And this module design includes six modules as, NIPB module, ECG module, SpO2 module, as optional IBP module and CO2 modules can be taken into account.
The followings have been explained each and every module's function:
1. NIBP Module – It is collecting data of blood pressure, including systolic, diastolic and also the mean arterial pressure throughout the (NIBP) cuff. These cuffs are available in different sizes for adults, infants and neonates. And there are two modes on the patient monitor of NIBP measurements and one mode for adults, infants and the other mode for neonates.
2. ECG Module – It is collecting the respiration waveforms, heart rate, through the ECG electrodes & leads.
3. SpO2 Module - The SpO2 module collects the data of pulse rate, pulse oxygen saturation (SpO2) and SpO2 volume waveform via the SpO2 probe.
4. CO2 Module – This CO2 module is collecting EtCO2, InsCO2 and the date of respiration rate through the sampling tube.
5. The Main Unit – This unit consists of the mainboard, keyboard, and the multi-function board. This multi-function board act upon the data communication among the ECG module, NIBP module, SpO2 module, CO2 module and the main module.
Uses/Benefits of Patient Monitors:
The patient monitor delivers high-quality care and lower risk. What does this device do is diagnosing, monitoring and recording the patient’s vital signs. Then it helps to identify the ailments and reduce the risks of a life at the early stage of the patient.
(i) To Maintain Diabetes:
In order to control diabetes, it should take care of the blood pressure, weight, blood glucose etc. For this, these diagnostic and monitoring devices assist the real-time delivery of blood glucose level and blood pressure helps or alert to the healthcare provider for treating when needed.
(ii) To Reduce the Risk of Heart Failure:
Due to the frenzied lifestyle, there are lots of people in the public community are suffering from different types of heart failures. Therefore to reduce the risk of these heart failure, there are devices such as pacemakers, cardiac resynchronization that brought by the technology in the market. This improves the quality of life and also helps to decrease the mortality rate and also the shortens of the duration of staying in the hospitals.
(iii) To Prevent Dementia and Falls:
When people are getting old, their sensory is impairment. Therefore people are at risk of having dementia and falls. In order to prevent these kinds of risks, and therefore this monitoring technology helps to prevent harm & promoting safety via continuous surveillance. There are different types of sensors that are attached to mobility devices. They are such as canes and walkers of the patient that alert of falling.
(iv) To Provide the Condition of the Patient to the Physician in Real-Time:
By checking the main screen of the monitor, the physician is able to understand the present condition of the patient in vital signs and start giving medication in real-time.
(v) To Monitor, the Patient’s Health Condition All the Time:
Therefore it would be easy to diagnose whether the patient is having a chronic disease or heart failure. This early diagnoses will help the patient to extend his/ her life
Accessories of the Patient Monitor:
There are many accessories for this device. Those are as follows considering the accessories sets for one patient monitor:-
(1) One set of ECG lead cable:
1. NIBP Module – It is collecting data of blood pressure, including systolic, diastolic and also the mean arterial pressure throughout the (NIBP) cuff. These cuffs are available in different sizes for adults, infants and neonates. And there are two modes on the patient monitor of NIBP measurements and one mode for adults, infants and the other mode for neonates.
2. ECG Module – It is collecting the respiration waveforms, heart rate, through the ECG electrodes & leads.
3. SpO2 Module - The SpO2 module collects the data of pulse rate, pulse oxygen saturation (SpO2) and SpO2 volume waveform via the SpO2 probe.
4. CO2 Module – This CO2 module is collecting EtCO2, InsCO2 and the date of respiration rate through the sampling tube.
5. The Main Unit – This unit consists of the mainboard, keyboard, and the multi-function board. This multi-function board act upon the data communication among the ECG module, NIBP module, SpO2 module, CO2 module and the main module.
Uses/Benefits of Patient Monitors:
The patient monitor delivers high-quality care and lower risk. What does this device do is diagnosing, monitoring and recording the patient’s vital signs. Then it helps to identify the ailments and reduce the risks of a life at the early stage of the patient.
(i) To Maintain Diabetes:
In order to control diabetes, it should take care of the blood pressure, weight, blood glucose etc. For this, these diagnostic and monitoring devices assist the real-time delivery of blood glucose level and blood pressure helps or alert to the healthcare provider for treating when needed.
(ii) To Reduce the Risk of Heart Failure:
Due to the frenzied lifestyle, there are lots of people in the public community are suffering from different types of heart failures. Therefore to reduce the risk of these heart failure, there are devices such as pacemakers, cardiac resynchronization that brought by the technology in the market. This improves the quality of life and also helps to decrease the mortality rate and also the shortens of the duration of staying in the hospitals.
(iii) To Prevent Dementia and Falls:
When people are getting old, their sensory is impairment. Therefore people are at risk of having dementia and falls. In order to prevent these kinds of risks, and therefore this monitoring technology helps to prevent harm & promoting safety via continuous surveillance. There are different types of sensors that are attached to mobility devices. They are such as canes and walkers of the patient that alert of falling.
(iv) To Provide the Condition of the Patient to the Physician in Real-Time:
By checking the main screen of the monitor, the physician is able to understand the present condition of the patient in vital signs and start giving medication in real-time.
(v) To Monitor, the Patient’s Health Condition All the Time:
Therefore it would be easy to diagnose whether the patient is having a chronic disease or heart failure. This early diagnoses will help the patient to extend his/ her life
Accessories of the Patient Monitor:
There are many accessories for this device. Those are as follows considering the accessories sets for one patient monitor:-
(1) One set of ECG lead cable:
(2) One set of NIBP cuff including for adults, paediatrics and infants:
(3) One piece of SpO2 probe including for adults and paediatrics:
(4) One piece of Body temperature probe:
(5) One piece of the Power supply cable:
(6) Ten pieces of Disposable electrodes:
(7) Printing paper rolls:
(8) CO2 probe (optional):
Types of Patient Monitors:
There are different types of patient monitors depend on the unit of the hospital. The patient monitor has been made out of different parameters depend on the necessity vital parameters to be checked/diagnosed of the particular unit of the hospital can choose the type of the patient monitor.
Therefore depend on the classification of the target parameter, there are types of monitoring as follows:
(1) Cardiac monitoring
(2) Respiratory monitoring
(3) Hemodynamic monitoring
(4) Neurological monitoring
(5) Blood glucose monitoring
(6) Body temperature monitoring
(7) Childbirth monitoring
(8) Cancer therapy monitoring
Therefore considering the compulsory parameters including the specific type of patient monitor can be used in the different units in the hospital.
Why Do We Need Patient Monitors:
Patient monitors are using to diagnose the early stages of life-threatening diseases such as heart failures etc... and reduce the risk of life-threatening for the patients. Considering the benefits of using this for both sides of patients and the doctors as follows:
For Patients :
• Well-timed & correct treatment at a premature stage.
• Reduced the wait time and travel.
• Several doctors are able to assess the condition from the inaccessible locations when using remote patient monitors.
• Immediacy to the community.
• Able to diagnose rapidly and fast involvement by the doctor.
For Doctors :
• Real-time revelation of medical parameters and patient health.
• Enhance operational efficiency, compliance & planning.
• Live streaming of patient data even in 2G network.
• Reduce workload and clinical productivity.
• Save the time & Resources.
Places Where These Devices are Used in the Hospital:
This patient monitor is using mostly in the Critical Care Unit (CCU) or Intensive Care Unit (ICU), Emergency Treatment Unit (ETU), Intensive Therapy Unit (ITU), Operations Theatres (OT), and sometimes for critical patients of medical and surgical wards.
The Appearance of the Patient Monitor:
Here can be considered the panel sections of the device as follows:
(1) Front Panel:
Here is the front panel of the device and can be seen some buttons on the bottom which can be switched.
Standard Measurements:
Here has been mentioned the normal ranges of each and every parameter of the patient monitor.
1. Ambient Temperature Range: 5℃~40℃
Relative humidity: 30%~80%
Atmospheric pressure: 70kPa~106kPa
Power supply: 100~240VAC
Power frequency: 50/60Hz
2. This apparatus must protect from direct sunlight, to prevent the high temperature inside of it.
3. Should not use in a toxic or inflammable gas environment.
4. Should be kept on a stand to prevent any possible shock.
5. Should not use with the combination in any other equipment that manufacturer has not been instructed.
6. When using this device with (ESU) electrosurgical unit, the operator (doctor or nurse) should pay attention to the safety of the patient.
7. Make sure the equipotential grounding terminal has grounded correctly.
8. Should not use the mobile phone nearby to avoid the strong radiant field interference.
Alarm Information:
(3) One piece of SpO2 probe including for adults and paediatrics:
(4) One piece of Body temperature probe:
(5) One piece of the Power supply cable:
(6) Ten pieces of Disposable electrodes:
(7) Printing paper rolls:
(8) CO2 probe (optional):
Types of Patient Monitors:
There are different types of patient monitors depend on the unit of the hospital. The patient monitor has been made out of different parameters depend on the necessity vital parameters to be checked/diagnosed of the particular unit of the hospital can choose the type of the patient monitor.
Therefore depend on the classification of the target parameter, there are types of monitoring as follows:
(1) Cardiac monitoring
(2) Respiratory monitoring
(3) Hemodynamic monitoring
(4) Neurological monitoring
(5) Blood glucose monitoring
(6) Body temperature monitoring
(7) Childbirth monitoring
(8) Cancer therapy monitoring
Therefore considering the compulsory parameters including the specific type of patient monitor can be used in the different units in the hospital.
Why Do We Need Patient Monitors:
Patient monitors are using to diagnose the early stages of life-threatening diseases such as heart failures etc... and reduce the risk of life-threatening for the patients. Considering the benefits of using this for both sides of patients and the doctors as follows:
For Patients :
• Well-timed & correct treatment at a premature stage.
• Reduced the wait time and travel.
• Several doctors are able to assess the condition from the inaccessible locations when using remote patient monitors.
• Immediacy to the community.
• Able to diagnose rapidly and fast involvement by the doctor.
For Doctors :
• Real-time revelation of medical parameters and patient health.
• Enhance operational efficiency, compliance & planning.
• Live streaming of patient data even in 2G network.
• Reduce workload and clinical productivity.
• Save the time & Resources.
Places Where These Devices are Used in the Hospital:
This patient monitor is using mostly in the Critical Care Unit (CCU) or Intensive Care Unit (ICU), Emergency Treatment Unit (ETU), Intensive Therapy Unit (ITU), Operations Theatres (OT), and sometimes for critical patients of medical and surgical wards.
The Appearance of the Patient Monitor:
Here can be considered the panel sections of the device as follows:
(1) Front Panel:
Here is the front panel of the device and can be seen some buttons on the bottom which can be switched.
 |
| The front panel of the patient monitor. |
1. Power button.
2. AC power indicator.
3. DC power indicator of in-built battery
4. ECG lead selection for shifting the ECG monitoring circulatory among the leads ofⅠ, Ⅱ, and Ⅲ AVL, AVF and V.
5. Alarm silence for 2 min, 5 min, 10 min and 20 min.
6. Freeze for analyze the ECG waveform segments for analyzing according to the system setting.
7. NIBP button to start or stop the NIBP measuring.
8. Print button to print out the ECG wave form.
(2) Rear Panel:
In this rear panel, the main port is the AC power supply socket. Instead of these ports, can be seen the following detailed nameplate of the device.
 |
| Nameplate of the patient monitor |
1 – CE mark
2 – Serial number
3 – Date of manufacturer
4 - Authorized representative in the European community
5 - Manufacturer (including address)
6 - Disposal of this device according to WEEE regulations
(3) Left and right panel:
 |
| Left and right panel |
In this figure from left to right shows in order as left panel and the right panel. The left panel consists of a built-in printer. In the right panel consists of the cable and the probe ports such as:-
1. TEMP probe connector
2. NIBP hose connector
3. SpO2 probe connector
4. ECG cable connector
5. The cable connector of CO2 sensor module
6. Cover of the battery compartment
Components of the Patient Monitor:
There are components as follows:-
1. Sensors – Biosensors such as to measure temperature, SPO2, EtCO2, etc and mechanical sensors are using here.
2. Analog to Digital converter – Converting all the physiological biosignals into a readable digital format which can display on the monitor screen.
3. Display / Output – The screen may be CRT, LED, or LCD. These display devices mostly used digital signal processing (DSP) and are able to track the different vital signs at the same time. This DSP has portability and miniaturization as advantages.
Block Diagram of the Patient Monitor:
The following figure shows the block diagram of the patient monitor. According to that the Physiological signals / the biosignals are coming from the patient of different parameters are detected by the specific transducers. These transducers then convert the physiological signal into an electrical signal which is amplified then and accustomed.
Then that signal passes through to the analogue to digital converter (ADC). Then this converter is sending the data to a microprocessor which is a based signal processor that extracts features such as blood pressure and heart rate.
After processing all these signals are displayed on a display/output device to monitor the condition of the patient.
 |
| Block diagram of the patient monitor. |
Here has been mentioned the normal ranges of each and every parameter of the patient monitor.
 |
| The main screen of the patient monitor |
This above figure shows the main screen of the patient monitor and it clearly declares the normal range measurements of each and every parameter. And it’s described more as follows:-
1. ECG
—Heart Rate or Pulse Rate(①unit:bpm)
—pacer detection (PACE②)
—ST-segment of channel 1 and channel 2 (③unit: mv)
— PVCs times (④ Unit: times/minute)
2. SpO2
—SpO2(⑤ unit:%)
—Pulse Rate(unit:bpm)
3. IBP (optional)
— Invasive Blood Pressure
(From left to right) Systolic, Diastolic, Mean (⑥Unit: mmHg or KPa)
4. NIBP
— None-Invasive Blood Pressure
(From left to right) Systolic, Diastolic, Mean (⑦Unit: mmHg or KPa)
5.RESP
—Respiration Rate(⑧unit:bpm)
6.TEMP
—Temperature(⑨unit: or℃℉)
7.CO2 (optional)
—end-tidal CO2 (⑩ Unit: mmHg or KPa)
—inspiratory CO2 ((11) Unit: mmHg or KPa)
—Air-Way Respiration Rate (AWRR),unit:bpm)
Operating Environment of the Patient Monitor:
The following environment should provide to the patient monitor to be functioned well:-
1. Ambient Temperature Range: 5℃~40℃
Relative humidity: 30%~80%
Atmospheric pressure: 70kPa~106kPa
Power supply: 100~240VAC
Power frequency: 50/60Hz
2. This apparatus must protect from direct sunlight, to prevent the high temperature inside of it.
3. Should not use in a toxic or inflammable gas environment.
4. Should be kept on a stand to prevent any possible shock.
5. Should not use with the combination in any other equipment that manufacturer has not been instructed.
6. When using this device with (ESU) electrosurgical unit, the operator (doctor or nurse) should pay attention to the safety of the patient.
7. Make sure the equipotential grounding terminal has grounded correctly.
8. Should not use the mobile phone nearby to avoid the strong radiant field interference.
Alarm Information:
 |
| Information about the Alarm system of the Patient monitor |
Working Principle of the Parameters of the Patient Monitor:
1. Measuring principle of the NIBP monitoring:-
In here the blood pressure of the patient is measured in a non-invasive way. This non-invasive way also includes different methodologies such as oscillating method and the ‘knockoff’ sound method that determines the systolic and diastolic blood pressure that detects the arterial sound using a stethoscope. This is applied to the brachial artery distal to the blood pressure cuff of the sphygmomanometer that is changing with cuff pressure.
Here using the oscillating method that the air will be filled by an inflation pump and release it slowly. Then the computer will record the change of the cuff pressure. Then the blood pressure value will be determined with this record.
2. Measuring principle of the SPO2 monitoring:-
For this monitoring, the method uses is the ‘Lamber-Beer’ law that is the absorption of the light of a given material. This is directly proportional to the concentration or its density. There is a different absorption range for oxygenated and deoxygenated haemoglobin (HbO2 and Hb) of the blood.
Therefore SpO2 measured by this patient monitor is the functional oxygen saturation as a percentage of haemoglobin that can be transported by oxygen.
3. Measuring principle of the respiration monitoring:-
Chest volume of the human lungs changes due to the volume of air filling inside to that when inhaling and releasing the air when exhaling. The conductivity of the body tissues are higher than the air. Therefore due to this inflation, the chest impedance will be changed.
Thus with this specialization respiration can be measured by sending a high frequency than the ECG, through the ECG electrodes to be measured the ECG signal as well as the chest impedance at the same time. Finally, it will be able to measure the respiratory rate according to an impedance method by using the software.
4. Measuring principle of temperature monitoring:-
It is using a sensor of thermo-resistor type (25℃, 5kΩ) which has supplied with a constant microcurrent. This temperature monitoring can be done in two different measuring methods such as measuring the body surface temperature and also through the temperature inside the body cavity (placed in anus or mouth).
5. Measuring principle of the CO2 monitoring:-
Here uses an IR beam and it is passed through a breathing gas sample and it is detected by a photodetector. Then this IR beam energy is absorbed by CO2 of this gas sample. Therefore the absorbed energy is directly proportional to the CO2 concentration of the gas sample.
Then to get the final output can be calibrated with a known value of CO2 concentration that is stored in the monitor’s memory according to the response of the photodetector. Finally, it displays as a numerical value in millimetres of mercury (mmHg) as a percentage (%), or kilopascals (kPa).
Troubleshooting:
There are some failures or troubles which may occur. Therefore following instructions can be followed to eliminate the problem:-
1. If the screen is not displayed -
• Shut down and unplug the AC power cable of the machine and check whether there is showing the proper voltage and check the continuity of the fuse using a universal meter.
• And also check the power cable wire and the socket, to check if there is any damage occurred and whether it is properly connected to the device.
2. If shows the external interferences of the ECG waveform on the monitor screen ;
• Check the ECG lead wires are broken or connected properly to the monitor.
• Check the ground wire of the monitor is properly grounded.
• Check the electrodes whether valid is using which connecting to the patient.
3. Not showing the NIBP range and the oxygen saturation of the monitor screen ;
• Make sure the blood pressure cuff has a leakage and it has been properly wrapped on the patient’s arm.
• Make sure that the patient is not talking or not engaging with any other work during getting the measurements of the blood pressure.
• Check the SPO2 probe is properly connected to the patient and the monitor
• Check whether the bulb is not blinking of the SPO2 probe when it’s connected to the patient.
• Still the problem is remaining contact the manufacturer.
4. The alarm system is not working properly ;
• Check whether the alarm limit value is proper for the condition of the patient.
• Check the probe connections.
• Check the lead connection.
Maintenance of the Patient Monitor:
There are some maintenance tips that can be carried out:
- Checking the monitor to verify whether there is any mechanical damage.
- Inspecting the exposed parts, inserted parts of all leads, and the accessories of the device.
- Examining all functions of the monitor of all parameters which is used for patient monitoring at the time, and make sure that all is in good working condition.
- Make sure that the earth wire of the monitor is grounded properly.
- Pay close attention to the fluctuation of the local power supply voltage.
References:
- Annicchiarico R, Cortés U, Urdiales C. Switzerland: Birkhäuser Verlag; 2008. Agent Technology and e-Health
- Blumenthal D. Stimulating the Adoption of Health Information Technology. N Engl J Med. 2009
- Cresswell K, Sheikh A. Organizational issues in the implementation and adoption of health information technology innovations: An interpretative review. International journal of medical informatics. 2013
- Isern D, Sánchez D, Moreno A. Agents applied in health care: A review. International journal of medical informatics. 2010
- Mohammadzadeh M, Safdari R, Rahimi A. Multi-Agent System as a New Approach to Effective Chronic Heart Failure Management: Key Considerations. Healthc Inform Res. 2013 Sep;19
- Paré G, Moqadem K, Pineau G, St-Hilaire C. Clinical Effects of Home Tele monitoring in the Context of Diabetes, Asthma, Heart Failure and Hypertension: A Systematic Review. J Med Internet Res. 2010
Monday, April 13, 2020
ECG (Electrocardiogram).
Overview:
History:
In 1902 Dr.William Einthoven was able to publish the first electrocardiogram recorded on a string galvanometer.
Introduction:
Sensor devices are using to identify and detect the electrical elements producing by heart every time it hits. The machine is recording these signals and a doctor checks the ECG waveform. An ECG can be prescribed or requested by a cardiologist (s) or any physician who thinks you may have a heart problem. The analysis can be performed by a medical specialist at a hospital, a hospital or your general physician.
Uses Of ECG Machine:
ECG also is known as the EKG which is an abbreviation of the word of the electrocardiogram. ECG that stands for Electro Cardio Gram which is a diagnostic tool used for detecting & recording the electrical activity of the heart.
History:
Considering the history of this device, there are 3 important persons can be declared as follows.
1. Dr.Alexander Muirhead
2. British Physiologist Dr.Augustus D.Waller
3. Dutch Physiologist Dr.William Einthoven
In 1902 Dr.William Einthoven was able to publish the first electrocardiogram recorded on a string galvanometer.
 |
| Dr.William Einthoven |
Einthoven was born in 1860 in Indonesia. Before his time, it’s known that Electric currents were produced by blows heart, but this phenomenon could not be quantified exactly without electrodes directly on it. Einthoven's heart completed a series of prototypes wired galvanometers in 1901. Between very strong electromagnets the machine used a thin conductive filament.
The electromagnetic field this would origin the sequence to move at the time the chain passed through the filament. This series would direct a shadow over the delicate role of photo paper when the light was shining. The innovative machine requires cooling water for advanced electromagnets. It took 5 people to manage and weighed about 600 lbs.
This machine has increased the sensitivity of the typical galvanometer to electrical activity of the heart can be measured despite the isolation of flesh and bones. Einthoven went on to describe the electrocardiographic characteristics of many of cardiovascular disease after developing the galvanometer with cords. Later Einthoven studied acoustics, especially the sounds of the heart that he had investigated with Dr.P Battaerd. After that, he died in Leiden and was buried in the reformed cemetery Haarlemmerstraatweg Church in Oegstgeest.
The electromagnetic field this would origin the sequence to move at the time the chain passed through the filament. This series would direct a shadow over the delicate role of photo paper when the light was shining. The innovative machine requires cooling water for advanced electromagnets. It took 5 people to manage and weighed about 600 lbs.
This machine has increased the sensitivity of the typical galvanometer to electrical activity of the heart can be measured despite the isolation of flesh and bones. Einthoven went on to describe the electrocardiographic characteristics of many of cardiovascular disease after developing the galvanometer with cords. Later Einthoven studied acoustics, especially the sounds of the heart that he had investigated with Dr.P Battaerd. After that, he died in Leiden and was buried in the reformed cemetery Haarlemmerstraatweg Church in Oegstgeest.
Introduction:
An electrocardiogram is a record of electrical impulses generated inside the heart. These impulses cause contraction of the heart muscle. The vector terminology is used to describe electrical impulses.
Vector is a schematic method that shows the strength and direction of electrical impulses. Vector
add them in the same direction and cancel if they point in the opposite direction. However, when they are at an angle to each other, they subtract or add the energy and thus, change the direction of flow.
Sensor devices are using to identify and detect the electrical elements producing by heart every time it hits. The machine is recording these signals and a doctor checks the ECG waveform. An ECG can be prescribed or requested by a cardiologist (s) or any physician who thinks you may have a heart problem. The analysis can be performed by a medical specialist at a hospital, a hospital or your general physician.
Uses Of ECG Machine:
ECG is an adhesive used by other diagnostic tests to help identify and monitor the cardiovascular disease.
Some heart problems, such as fixation, dizziness, dizziness and lips can be used for a symptom investigation.
• Allows detecting the abnormalities of conduction.
• Use to identify a prior heart attack.
• Important in non-cardiac diseases. Ex:- Hypothermia, Pericarditis, Chamber hypertrophy, Arrhythmias.
• Helps detect electrolyte disturbances.
• Measure heart rate and heart rhythm.
Types of the ECG Machine:
ECG machine consists of Unipolar & Bipolar electrodes, amplifiers, connecting wires, output /display.
And there are two types of ECG machines called:
- Single Channel which consists of one recording system and one amplifier.
- Multi-Channel devices which have 12 standard leads configuration that detects heart signal using a microprocessor.
Single Channel ECG Machine: Multi-Channel ECG Machine:

Accessories of the ECG machine:
They are as follows:
1. ECG Clamps
These clamps are connected as the limb leads to the patient’s right arm, left arm, right leg, left leg.
2. Patient Cable
This patient cable is connected to the ECG machine and the other ends of the cable are connecting to the leads. This cable is designed to measure the ECG and the impedance respiration of the patients.
3. Chest Electrodes

 There are six chest electrodes/bulbs are used to detect primarily the heart’s frontal plane electrical activity.
There are six chest electrodes/bulbs are used to detect primarily the heart’s frontal plane electrical activity.
4. ECG Gel
This ECG gel is used to improve the conductivity between the electrodes and the skin of the patient.
ECG Paper Roll
On this paper, the electrical activity of the heart is recorded and printed. These papers are made of as water-resistant.
Preparation for the ECG Test:
There are diverse ways to perform an ECG. The test generally involves performing a number of sticky, small sensors, known as electrodes in the chest, arms and legs. They are attached to the ECG recording device. There is nothing special preparing for the patient for the test. You can usually drink and eat in advance.
At first, need to remove the topcoat, and breasts may need to be cleaned before going to attach the electrodes. Hospital clothing cover may be given as soon as the electrodes are placed.
The test takes a few seconds for recording and you must go home immediately or return to the hospital if you are already in a hospital.
Considering the procedure of preparing the Electro Cardio Graph, in the heart, it’s producing tiny electrical impulses which spread through the myocardium or the heart muscle to make the cardiac contract. Therefore ECG device is important to represent in composite action of potential that is generated by depolarization and repolarization of all cardiac cells which have the following physiological properties:
• Automaticity – Ability to initiate an impulse
• Excitability – Ability to respond to a stimulus
• Conductivity – Ability to transmit an impulse
• Contractility – Ability to respond with pumping action of the heart
Types of ECG Tests:
There are three types of ECG Tests.
How ECG Machine Works:
Switch on the ECG machine and check the ECG display/monitor parameters and all the accessories are cleaned and ready to connect to the patient. When the electrical signals are generating through the heart, by the connected ECG electrodes, it’s recorded the timing and the potential of the signal in a graph on the ECG display/ monitor. Therefore after connecting the machine to the patient leave 1-2 minutes and then start to record the ECG trace of the heart
Einthoven's Triangle and this theory applied in ECG device. This Einthovans triangle uses in the Electrocardiography as imaginary triangle using three limb leads to check whether there is incorrect placement of the leads of the patient. According to Einthoven's law, the ECG machine records the activity which is taken the three limb leads simultaneously. And the following relationship equations of these three bipolar limb leads can be declared as given below.
1) I+II+III=0
2) I+(-II)+III=0
3) I+III=II
Therefore the summation of the electric potential of any two bipolar limb leads out of the three limb leads is equal to the value of the other third bipolar limb lead.
Block Diagram of the ECG Machine:
• It’s a muscular organ & it looks cone shape .
• Base is located above and apex is located below.
• The inclination of the heart at the left side
• Approx weight of it is 300gms
• Consists of two atriums & two ventricles separated by valves
Conduction Physiology of the Heart:
Location of the SA (Sinoatrial) node and AV (Atrioventricular) node in the right atrium of the heart is important to generating electric impulses of the heart.
Therefore the system of the electrical conduction of the heart is beginning by generating electric impulses in the SA node also acknowledged as the pacemaker of the heart. Then it spreads throughout the internodal routes to the AV node. This AV node is conscientious for transmission of the impulse as of the atria to the ventricles. There is a delay while the depolarization and this impulse continuous throughout the AV bundle & behind the left and right bunch of branches of the ‘Purkinje fibers’. This bundle conduct the impulsion to ventricles covering all parts of myocardium cells causing contraction due to action potential.

Accessories of the ECG machine:
They are as follows:
1. ECG Clamps
These clamps are connected as the limb leads to the patient’s right arm, left arm, right leg, left leg.
2. Patient Cable
This patient cable is connected to the ECG machine and the other ends of the cable are connecting to the leads. This cable is designed to measure the ECG and the impedance respiration of the patients.
3. Chest Electrodes

 There are six chest electrodes/bulbs are used to detect primarily the heart’s frontal plane electrical activity.
There are six chest electrodes/bulbs are used to detect primarily the heart’s frontal plane electrical activity.4. ECG Gel
This ECG gel is used to improve the conductivity between the electrodes and the skin of the patient.
ECG Paper Roll
On this paper, the electrical activity of the heart is recorded and printed. These papers are made of as water-resistant.
Preparation for the ECG Test:
There are diverse ways to perform an ECG. The test generally involves performing a number of sticky, small sensors, known as electrodes in the chest, arms and legs. They are attached to the ECG recording device. There is nothing special preparing for the patient for the test. You can usually drink and eat in advance.
At first, need to remove the topcoat, and breasts may need to be cleaned before going to attach the electrodes. Hospital clothing cover may be given as soon as the electrodes are placed.
The test takes a few seconds for recording and you must go home immediately or return to the hospital if you are already in a hospital.
Considering the procedure of preparing the Electro Cardio Graph, in the heart, it’s producing tiny electrical impulses which spread through the myocardium or the heart muscle to make the cardiac contract. Therefore ECG device is important to represent in composite action of potential that is generated by depolarization and repolarization of all cardiac cells which have the following physiological properties:
• Automaticity – Ability to initiate an impulse
• Excitability – Ability to respond to a stimulus
• Conductivity – Ability to transmit an impulse
• Contractility – Ability to respond with pumping action of the heart
Types of ECG Tests:
There are three types of ECG Tests.
- Resting ECG – while you're lying down in a comfortable position
- Stress or Exercise ECG – while you're using an exercise bike or treadmill
- Ambulatory ECG – the electrodes are connected to a small portable machine worn at your waist so your heart can be monitored at home for 1 or more days
How ECG Machine Works:
Switch on the ECG machine and check the ECG display/monitor parameters and all the accessories are cleaned and ready to connect to the patient. When the electrical signals are generating through the heart, by the connected ECG electrodes, it’s recorded the timing and the potential of the signal in a graph on the ECG display/ monitor. Therefore after connecting the machine to the patient leave 1-2 minutes and then start to record the ECG trace of the heart
Einthoven's Triangle and this theory applied in ECG device. This Einthovans triangle uses in the Electrocardiography as imaginary triangle using three limb leads to check whether there is incorrect placement of the leads of the patient. According to Einthoven's law, the ECG machine records the activity which is taken the three limb leads simultaneously. And the following relationship equations of these three bipolar limb leads can be declared as given below.
1) I+II+III=0
2) I+(-II)+III=0
3) I+III=II
Therefore the summation of the electric potential of any two bipolar limb leads out of the three limb leads is equal to the value of the other third bipolar limb lead.
 |
| Einthoven’s Triangle |
Block Diagram of the ECG Machine:
This is a block diagram of a basic single-channel ECG machine and the dotted line of the diagram shows the separation of the circuit for patient’s protection between the operation circuit from isolated supply and the main power supply.
Anatomy of the Heart:
Anatomy of the heart can be pointed out as follows-
 |
Anterior view of the human heart. |
• Base is located above and apex is located below.
• The inclination of the heart at the left side
• Approx weight of it is 300gms
• Consists of two atriums & two ventricles separated by valves
Conduction Physiology of the Heart:
Location of the SA (Sinoatrial) node and AV (Atrioventricular) node in the right atrium of the heart is important to generating electric impulses of the heart.
 |
| Conduction system of the heart. |
The most popular cardiac controller or the pacemaker is the SA node. Atrial cell, AV node, its node, ligaments, Purkinje fibers and myocardial cells are other objects of cardiac stimulation. When the SA node fails, they can start the pulse slowly.
ECG Leads:
ECG device consists of 12 Leads. They are six limb leads and six chest leads.
Limb leads consist of unipolar three leads and bipolar three leads.
- V1- fourth intercostal space at the right sternal border
- V2- fourth intercostal space at the left sternal border
- V4- fifth intercostal space at the midclavicular line
- V3- midway between V2 and V4
- V5- at the same horizontal level as V4 in the anterior axillary line
- V6- at the same horizontal level as V4 in the midaxillary line.
The limb leads I, II and III are the bipolar limb leads and the other three leads are the limb electrodes those are the unipolar limb leads.
The pair of electrodes, which consists of a neutral conductor and an extremity electrode. "Reference line" that was created by connecting the additional two limb positions of the ECG amplifier to the negative electrode.
Or else in other side, Each line has the positive end on the consequent limb line and runs straight to heart, the place of its "negative" end involving between the other two limbs. These are considered to be as guide augmented unipolar limbs.
The voltage recorded linking the left arm is the limb lead and the neutral reference lead is called Lead aVL; The right arm limb guide is also aVR and the left Leg guide is aVF.
The following diagram shows the ECG electrodes placement of the human body and the relevant recordings of each and every electrode’s configurations.
 |
| Anatomical representation of the placement of the electrodes |
Measuring ECG:
Normally the ECG is measured from the skin surface, what can be done by placing two electrodes directly on the skin and read the possible difference between them. This is possible because these signals are sent throughout the body.
Again, as noted above, the characteristics of the detected waveform depend not only in the amount of heart tissue involved, but also further orientation of the electrodes relative to the dipole. That is, the ECG waveform appears small different when measured from different electrode positions, and ECG is usually obtained using different electrodes locations or settings, which is lucky standardized by the general application of certain conventions.
Components of the ECG trace:
Typical ECG wave form as follows-
 |
ECG waveform |
• P Wave – Depolarization of atriums. Time taken 0.08s - 0.1s
• QRS Complex – Depolarization of ventricles. Time taken 0.06s – 0.1s
• T Wave – Repolarization of ventricles.
Safety and Precautions for the Machine:
Before going to connect the device to the patient following points should be considered to get an accurate electrocardiograph.
• Always keep the device in a dust-free environment avoiding moisture.
• Should isolate the device from electronic devices, mobile phones, radiography equipment.
• Use 3 prong power supply cable with the machine.
• Make sure always the ECG Patient cable is not tied prevent damaging.
• Properly cleaned the gel of the ECG electrodes and ECG bulbs.
• Always check whether there is sufficient paper roll.
• Clean the thermal printer head.
• Check the display whether it’s showing the measurements of the parameters including speed, date, patient details, etc...
Taking into account the above points as Preventive Maintenance for the device and now it is totally ready to be functioned. In order to get the betterment result, should advise the patient not to tremble the body and not to talk.
Then apply enough gel on the cleaned limb and chest electrodes, and place on the body properly.
Before going to print the paper let give few minutes to reduce disturbances affecting from noises and diagnose the chest leads readings and record it on the ECG thermal paper.
Troubleshooting:
There are some troubleshooting techniques that can be considered as follows-
Article Contributed By:-
Subscribe to:
Posts (Atom)



























