Colonoscopy is an examination to inspect the inner lining of the large bowel (rectum and colon) for polyps (lumps inside your colon that can turn into cancer) using a thin flexible tube called colonoscope with a camera at its tip.
It is inserted via the anus and gently guided to the start of the large bowel and also it is possible to enter and examine the last few inches of the small intestine (terminal ileum).
Colonoscopy can detect inflamed tissue, ulcers and abnormal growths and commonly used to evaluate gastrointestinal symptoms. This procedure is used to look for early signs and also it acts as a:-
- Screening test for colon cancer.
- Investigate abdominal pain, rectal bleeding and chronic constipation/diarrhoea.
HISTORY OF THE COLONOSCOPY:
- In the early 1960’s DR.Niwa and DR.Yamagata at Tokyo university developed the device.
- Later the endoscopic excision of polyps from anywhere in the colon began in June and September of 1969.
- Momentous advances have occurred over the past two decades and the two procedures are now widely accepted and practised.
- The doctor uses the colonoscopy, a long, flexible, tubular instrument that transmits an image of the colon, the colonoscope is inserted through the rectum and advanced to the other end of the large intestine.
- Another procedure is you will lie on the table while the technician places a small tube inside your rectum to fill your colon with air. The table is moved into the CT machine where it is scanned. The air helps to create clear images.
WHY COLONOSCOPY IS DONE:
Your concerned doctor may recommend a colonoscopy for the upcoming reasons:
- TO INVESTIGATE INTESTINAL SIGNS AND SYMPTOMS: A colonoscopy can help your doctor explore possible causes of abdominal pain, blood in rectal, chronic constipation, severe diarrhoea and some other related problems.
- SCREEN FOR COLON CANCER: If you cross the age of 50 and above you have a maximum risk for colon cancer. sometimes the symptoms may not show you properly on time for every 5 or 10years you have recommended taking a colonoscopy.
- LOOK FOR MORE POLYPS: If you have polyps already, your doctor may recommend a follow-up colonoscopy to look for and remove any additional polyps. This is done to reduce your risk of colon cancer.
COMPONENTS OF THE COLONOSCOPY:
 |
| PARTS OF THE COLONOSCOPE. |
- Control section – it provides a distal and bending section.
- Instrument channel (forceps, snare, injector and clip device).
- Objective lens, light guide, water jet nozzle, working channel - colonoscopes have several hollow channels for suction, water and air delivery for the purpose of insertion of the accessory instruments, the light guide is for better viewing.
- A tip (The distal end of the shaft, controlled from the control section) – It includes a charge-coupled device that serves as a small camera and electronically transmits the image from the CCD to an external video-processing unit.
- A connection section and line.
IS THAT ANY PREPARATION NEEDED BEFORE COLONOSCOPY?
Before the colonoscopy, some preparing procedures are there for the patients who undergo colonoscopy this process is known as Bowel Prep.
Generally, the solids must be emptied from the gastrointestinal tract.
- WHETHER THEY FOLLOW A SPECIAL DIET THE DAY BEFORE THEY EXAMINE?
- Of course, they won’t eat any foods they have a liquid diet for 1 or 3 days before i.e any solid foods the day before the colonoscopy. Limited clear liquid items only consumed such as water, tea, black coffee(without milk), broth and carbonated beverages. They won’t allow you to eat flavoured/coloured (red dye) beverages sometimes it may confuse with the blood. And also you can eat low fibre food no whole grains, nuts or seeds
- CAN I CONSUME ANY BLOOD THINNER DRUGS?
- Most medications may be continued as usual but the medication with the blood thinners such as warfarin, insulin, aspirin, arthritis medication and iron preparations are some medicine need to consulted with your doctor.
- DID I UNDERGO ANY DENTAL PROCEDURES?
- The doctors should be altered if, in the past, patients have required antibiotics prior to surgical or dental procedures to prevent infections.
- CAN I DRIVE BEFORE THIS PROCEDURE?
- Driving is not permitted for 24 hours after colonoscopy to allow the sedative time to wear off. Before the procedure, the patient made some plan for riding from the home hospital.
- IS THAT ANY PREPARATION LEFT?
- Yes, A laxative or an enema may be required the night before colonoscopy. A laxative is a medicine that loosens stool and increases bowel movements. This is usually swallowed in the form of a pill or as a powder that is dissolved in water. An enema is performed by flushing water, or sometimes a mild soap solution, into the anus using a special wash bottle.
PROCEDURE FOR COLONOSCOPY:
Colonoscopy is a low-risk safe procedure with low complications. The most significant risk is that its perforation of the bowel.
1. During a colonoscopy procedure, you will wear a gown. Sedation (Anaesthesia) is usually recommended. Sometimes mild sedation is given to the pill form. In other cases, a sedative is combined with intravenous pain medication to minimize any discomfort. It feels the patient to be relaxed.
2. During the examination, a patient lies on their left side on an examination table. The doctor and medical staff monitor vital signs and attempt to make patients as comfortable as possible.
3. Usually, your knees were drawn toward your chest. The patient is continuously monitored for heart rate/rhythm, blood pressure and oxygen in the blood.
4. The colonoscope which is long enough (adult colonoscope length 160cm, Intermediate colonoscope length 130cm) to reach the entire length of your colon. It contains a light and a tube that allows the doctor to pump air or carbon dioxide (CO2 reduces the post-procedural pain) into your colon. This air inflates the colon, which provides a better view of the lining of the colon.
5. Once the tip of the colon (cecum) or the last portion of the small intestine (terminal ileum) is reached, the colonoscope is slowly withdrawn, and the lining of the colon is carefully examined.
6. Colonoscope may often make you feel bloating and cramping in the abdomen area or the urge to have a bowel movement but with the medication pain becomes infrequently causes severe pain and it is tolerated.
7. The camera sends images to an external monitor so that the doctor can study the inside of your colon.
8. A colonoscopy usually takes 15 to 60 minutes. If the entire colon, for some reason cannot be visualized, the physician may decide to try colonoscopy again at a later date with or without different bowel preparation or may decide to order an X-ray or CT of the colon.
9. The doctor can also insert the colonoscope through the channel to take a biopsy (tissue sample) or remove polyps or other abnormal tissue.
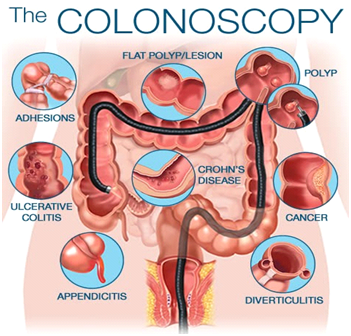
ABNORMALITIES DETECTED DURING COLONOSCOPY:
If a colonoscopy is negative i.e your doctor doesn’t find any abnormalities in the colon during the procedure. They may recommend that you have another colonoscopy in the next year, 5 years or 10 years
ONE YEAR: In one year if there was a residual stool in the colon that prevented complete examination of your colon.
FIVE YEARS: In five years if you have a history of polyps in previous colonoscopy procedures.
TEN YEARS: In ten years if you are at average risk of colon cancer-you have no colon cancer other than that.
If the colonoscopy is positive i.e your doctor finds abnormalities in the colonoscopy.
 |
| ABNORMALITIES DURING COLONOSCOPY. |
If it is positive the doctors find any polyps or abnormal tissue in the colon. Most of the polyps are not cancerous, but some can be precancerous. During the colonoscopy, the removed polyps are sent to the laboratory for testing and analysing to determine where the polyps are cancerous, precancerous or noncancerous.
Based on the size and the polyps number you may need to follow rigorous surveillance for the future.
If your doctor finds one or more with less than 0.4inch in diameter, the patient may recommend a repeat colonoscopy in further years. Depending on the other problems /Risk for colon cancer they are:
 |
| COLON POLYPS |
- Cancerous polyps
- Some certain characteristics of the polyps indicate high-risk possibilities of colon cancer.
- If the polyps are larger than 0.4 inches.
- If you have a polyp or any other abnormal tissue that couldn’t be removed during the colonoscopy, your doctor may recommend a repeat examination in the gastrointestinal tract specialist(gastroenterologist) who is special expertise in removing large polyps, or surgery.
 |
| COLON CANCER THAT FINDS DURING DIAGNOSIS OF COLONOSCOPY. |
RISK AND COMPLICATIONS OF THE COLONOSCOPY:
- A colonoscopy poses few risks and rare complications of a colonoscopy may include
- Adverse reaction to the sedative used during the exam.
- Bleeding from the site where a tissue sample (biopsy) was taken or a polyp or other abnormal tissue was removed.
- A tear in the colon or rectum wall (perforation).
- Inflammation or infection of pouches in the colon known as diverticulitis.
- A severe problem in abdominal pain, and problems in people with heart or blood vessel disease.
- Some complications can lead to blood transfusions, surgery, hospitalization or rarely death.
VIRTUAL COLONOSCOPY :
CT colonoscopy or virtual colonoscopy is a medical imaging procedure which uses X-rays and computers to produce two and three-dimensional image of a colon. It includes images of the large intestine, small intestine and colon. CT colonoscopy is mainly used to evaluate colorectal polyp detection, and it may be used for colorectal screening.
If your doctor is concerned about the quality of the view through the scope, he or she may recommend a repeat colonoscopy. If your doctor wasn’t able to advance the scope through your entire colon, a virtual/CT colonoscopy is recommended to examine the rest of your colon.
HOW SHOULD I PREPARE BEFORE THE PROCEDURE?
- The patient should wear comfortable loose clothing to your exam. They gave a gown to wear before the procedure.
- I suppose the pregnant women have an examination they priorly inform the CT technician so that they see the safety precautions before the procedure.
- The bowel cleaning procedure is the same as that of colonoscopy or it consists of some cleansing liquid.
- It is very important to take the liquid diet before the procedure and also it is very important to clean your colon the night before their CT colonoscopy.
- The patient will ask to take any laxative or pills, some common preparation is magnesium citrate and bisacodyl etc.
- Additional liquids such as barium and ionized liquids are taken before the examination.
- If the patient has any health issues such as heart, liver or kidney disease priorly inform to your concerned doctor so that the bowel preparation will be safe in some conditions.
- The patient will consume and start to resume their own normal diet after the procedure.
VIRTUAL COLONOSCOPY PROCEDURE:
1. The patient is asked to lie on their left side on a narrow table that is connected to a CT scan machine.
2. Knees will be up towards the chest. A small, flexible thin tube will be inserted into the rectum.
3. Air can be pumped through the tube to make the colon inflate(bigger) and make the colon for better viewing. After this is done, the patient will be asked to lie in the supine position.
4. The table moves through the scanner to produce a series of two-dimensional cross-sections along the length of the colon.
5. A computer program put these images together to create 3D pictures that can be viewed on the monitor.
6. To avoid distortion on the images, the patient is asked to hold their breath for a few seconds.
7. The scan is then repeated with the patient lying in a prone position.
8. After examination, the images produced by the scanner must be processed into a 3D image.
9. The patient may resume normal activity after the procedure. The is no post-procedure problems.
 |
| SUPINE AND PRONE POSITION DURING COLONOSCOPY |
DIFFERENCE BETWEEN VIRTUAL COLONOSCOPY AND NORMAL COLONOSCOPY:
- Virtual colonoscopy is less invasive and faster to perform than a traditional colonoscopy and does not require conscious sedation.
- In traditional colonoscopy no radiation is required, a low dose of radiation is required in virtual colonoscopy.
- Virtual colonoscopy is not as accurate as traditional in finding flat cancers.
- Virtual colonoscopy cannot remove polyps.
- The entire colon is screened in traditional colonoscopy, In virtual colonoscopy entire colon is screened and also it detects other issues in your abdomen.
- Traditional colonoscopy requires 45-60mintues whereas virtual colonoscopy requires 15 minutes.
- 5 to 6 feet tubing is required for a traditional colonoscopy, 2-3 inch probe is enough for virtual colonoscopy.
 |
| (a)(b)IMAGES TAKEN IN CONVENTIONAL COLONOSCOPE(c)VIRTUAL COLONOSCOPE |
 |
| IMAGES TAKEN IN VIRTUAL COLONOSCOPY |
RISK IN VIRTUAL COLONOSCOPY:
- There is a very precise risk that inflating the colon with air could injure or perforate the bowel. This most rarely occurs in one in 10,000 patients.
- There is always a slight chance of cancer from excessive exposure to radiation. However, the benefit of an accurate diagnosis far outweighs the risk.
- The effective radiation dose for this procedure varies.
- CT scanning is, in general, not recommended for pregnant women unless medically necessary because of the potential risk to the unborn baby.
BENEFITS OF VIRTUAL COLONOSCOPY:
- CT colonoscopy provides clearer and more detailed images than a conventional barium enema X-ray examination.
- CT colonography is less costly than coloscopy.
- No radiation remains in a patient’s body after a CT examination.
- CT colonography is well tolerated. Sedation and pain relievers are not needed, so there is no recovery period and you can return to your normal daily activities immediately after the test.
- CT minimally invasive test provides both 2D and 3D images that can create many polyps and other lesions as clearly as when they are directly seen by conventional colonoscopy.
LIMITATIONS OF CT COLONOSCOPY:
- A person who is very large may not fit into the opening of a conventional CT scanner or may be over the weight limit.
- CT colonoscopy is strictly a diagnostic procedure. If any polyps found are found they will have to remove by conventional colonoscopy.
- CT colonoscopy may not differentiate stool from artefacts and smaller polyps.
- Colonoscopy is good only at detecting colorectal cancer found on the left side of the colon, why because the left side of the colon is sort of mushroom-shaped with a stem thus making them easier to see and remove whereas the right side often has squattier looking thus it looks flatter and harder to see.
- CT colonoscopy is not recommended for the patient having inflammation, bowel disease because of the increased risk of perforation.
TYPES OF COLONOSCOPIES:
There are two main types of colonoscopy screening and diagnostic colonoscopy.
SCREENING COLONOSCOPY:
- A screening colonoscopy is a preventive procedure for patients who have no symptoms of colon cancer.
- If a patient has any related symptoms or has any polyps removed during screening colonoscopy.
- A screening colonoscopy is recommended at the age of 50. If you are under the age of 50 you are not eligible for screening colonoscopy.
DIAGNOSTIC COLONOSCOPY:
- A diagnostic colonoscopy occurs when sample tissue must diagnose an unusual or abnormal-looking growth or section of tissue during a screening colonoscopy.
- Once the tissue is taken, a screening colonoscopy becomes diagnostic.
- The diagnostic colonoscopy is needed when the patient has the following symptoms such as a change in bowel habits, diarrhoea, constipation, rectal bleeding, anaemia, etc.
STERILIZATION AND CLEANING PROCEDURE OF COLONOSCOPY:
- A study done for the last few years by Canadian researchers discovered that up to 15% of the scopes at some centres contain “bio-dirt” which are cells and debris from prior exams.
- This bio-dirt can produce harmful microorganisms.
- There are several phases of the cleaning process first the technician wipes and flushes the colonoscope with a cleaning solution that is meant to get rid of bio-dirt.
- The colonoscope is then cleaned with 'MetriZyme' which is an enzymatic solution designed to break down and remove all debris.
- During this process, the technician uses long specialized brushes to clean in all the ports and buttons as well.
- The colonoscope is put into the machine and all the required tubes that wash the port are connected. Then wash them with the combination of Acecide-c ( a peracetic acid-based high-level disinfectant and sterilant).
- At last, it is flushed with 70% isopropyl alcohol. This process takes over ½ an hour per scope.
MAINTENANCE:
The maintenance of the colonoscope is important however this will be carried out by medical staff, clinical engineer, technician, a biomedical engineer and central processing technician for cleaning and disinfecting.
TROUBLE ARISE DURING COLONOSCOPY:
Difficulties causes during colonoscopy is that trouble in getting through the entire colon or fail to do so there are many reasons is there the main things are:
- One such is the presence of surgical adhesions, another factor is body habitus.
- Women are likely to have a difficult colonoscopy because it has been shown that they have longer colons than men packed into a smaller abdominal cavity, resulting in many twists and turns in the colon.
- The younger the person more pain will be experienced.
- During the colonoscopy, difficulty occurs in the sigmoid colon where it can be difficult to get around acute bends.
- The most common technical problem is that insertion of the scope based on the shape of the colon each anatomical part has its own characteristic shape, fixation and suspension.
HOW TO TROUBLESHOOT THESE PROBLEMS:
- The patients in whom it is difficult to get through the sigmoid colon it may be worthwhile for the colonoscopist to use a pediatric colonoscope, and also we can use a gastroscope, which due to the very short radius of curvature can easily negotiate the acute bends.
- A successful colonoscopy is to make and keep the sigmoid colon straight during and after the scope reaches the descending colon.
- Before using colonoscopes, calibration is must whether the cable is damaged or check any discontinuities that occurred. Thereby reduce the troubles while doing the procedure.
👉 Please Watch Our Colonoscopy Videos (Part 1 & Part 2) from Our YouTube Channel Below:-
1. Part 1 Video:-
2. Part 2 Video:-
REFERENCE:
- Lee SH, Lee DJ. Comparison of colonoscopic parameters according to the length of adult-colonoscope. Chin Med J (Engl) 2016;127:85–91. [Google Scholar]
- Varadarajulu S, Banerjee S, Barth BA, Desilets DJ, Kaul V, Kethu SR, Pedrosa MC, Pfau PR, Tokar JL, Wang A, et al. GI endoscopes. GastrointestEndosc. 2016;74:1–6.e6.
- https://www.webmd.com/colorectal-cancer/colonoscopy-what-you-need-to-know#1 (google scholar).









No comments:
Post a Comment