An endoscope is a thin, rigid, flexible instrument combined with fibre-optics and charge-coupled device to facilitate illumination or visualization of the interior organs. Endoscopy is a process in which the endoscope is passed through the mouth, into the oesophagus and down towards the stomach and duodenum. The tip of the endoscope contains the light and tiny video camera so that the doctor or operator can able to see inside your gut.
- The endoscope has a channel through which surgeons can manipulate tiny instruments, such as forceps, surgical scissors, and suction devices.
- A variety of instruments can be fitted to the endoscope for different purposes.
- Through one channel of endoscope water and the air is conducted to wash and dry the surgical site.
- Endoscope gives visual evidence of the problem such as ulceration or inflammation.
HISTORY OF THE ENDOSCOPE:
- In 1805, Philip Bozzini made the first attempt to observe the living human body directly through a tube, he created lichtleiter a light-guiding instrument.
 |
| IMAGE OF PHILIP BOZZINI AND LICHTLEITER ENDOSCOPE |
- In 1853, Antonie Jean Desormeaux of France specially designed to examine the urinary tract and the bladder. He named it as an endoscope.
 |
| IMAGE OF ANTONIE JEAN DESORMEAUX ENDOSCOPE |
- In 1868, Dr. Adolph Kussmaul of Germany succeeded in taking a look inside the stomach of a living human body.
 |
| IMAGE OF Dr.ADOLPH KUSSMAUL ENDOSCOPE |
- In 1932, Johann von Mikulicz and his associates created the 1st rigid gastroscope but it is not flexible.
- In 1932, Dr. Rudolph Schindler invented a flexible gastroscope that allows the examinations even while the tube is bent. This tube was 75 centimetres in length of the tube and 11 millimetres in diameter.
 |
| IMAGE OF Dr. RUDOLPH SCHINER FLEXIBLE GASTROSCOPE |
- In 1983 the first endoscope without fibre optic transmission of the image was produced by Welch Alleyn Incorporated in New York. At the tip of the instrument was an electronic sensor consisting of a packed grid of photocell receptors which transmitted images electronically to a video processor and then to a television monitor.
 |
| IMAGE OF WELCH ALLEYN ENDOSCOPE |
WHY ENDOSCOPY IS NEEDED?
The doctor may recommend an endoscopy for various reasons
- If the food pipe (oesophagus), stomach, or top part of the small intestine need to be looked at, then gastroscopy is needed.
- Endoscopy is needed for the early detection of cancer from the mucous covering in either the upper or lower tracts of the digestive tube.
- To find out helicobacter pylori infections, it is the bacteria are thought to cause gastric tumours.
- Gastroscopy is needed for the persons with gastroesophageal reflux disease or GERD, especially for the person, those who consume alcohol and smoke regularly and complain of chronic heartburn are at risk for cancer of the oesophagus.
- It is needed to find out the changes in the lining of your oesophagus.
IS THAT PREPARATION NEEDED FOR ENDOSCOPY?
Endoscopy (gastroscopy) requires special preparations:
- It is advisable to discontinue taking alcoholic beverages and also avoid nuts, seeds and spicy foods before the examination.
- The last meal before the diagnostic procedure must be no later than at 6 PM of the previous day.
- On the day of the examination, it is not allowed to take foods or beverages for 6 to 8 hours before the procedure, a little water can be taken no later 2-4 hours before the examination.
- If the patient takes any chronic medication in caps or pills such as any medicine that used to treat diabetics, such as insulin and metformin, any blood thinning medication ( i.e) low-dose aspirin, aspirin, warfarin or clopidogrel, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory medicine, they should suspend taking them since foreign items in the cavity of the organ being examined can distort the picture.
- It is very important to alert the doctor about any existing allergic reactions if they are associated with medical drugs.
- Before the examination the doctor will administer premedication or anesthetization of the base of tongue and throat with a spray, this will reduce discomfort and pain.
- If the patient has any heart valve disease and has pacemaker priorly inform to the concerned doctor.
- I suppose the patient may wear dentures they may be asked to remove them prior to their procedure.
- Patients are advised to leave their contact lenses at home and wear glasses instead.
IS THAT ANY PROCEDURE IS THERE DURING ENDOSCOPY (GASTROSCOPY)?
- The patient will be asked to lie flat, generally on the left side, before the procedure, your throat will be numbed with a local anaesthetic spray, you can choose to have sedative if you prefer. This means you will still be awake but will be drowsy and have reduced awareness about what’s happening.
- A smallmouth guard will put between our teeth to stop you from biting the endoscope and to protect the teeth.
- The endoscope will be placed into your mouth and you will be instructed to swallow it down to oesophagus and into your stomach.
- The doctor will direct air into your stomach via the gastroscope, this will make viewing easier.
- Sometimes a special instrument can be inserted through the scope, and a small sample of tissue removed (biopsy) This is not painful.
- Some treatments can be performed while the endoscope is in such as removing polyps, controlling blood loss from an ulcer, controlling or preventing bleeding from enlarged veins, a narrowed oesophagus can be widened.
COMPONENTS OF ENODOSCOPE:
- A thin, long flexible, rigid tube
- A lens or lens system
- A light-transmitting system
- The eyepiece
- Control system
- Water pipes
- The operational channel
- Control cables.
A THIN, FLEXIBLE, RIGID TUBE:
- FLEXIBLE: Flexible endoscope allows the user to navigate hard to reach areas by controlling the directional movement of the scopes distal end.
 |
| IMAGE OF FLEXIBLE TUBE |
- RIGID: Rigid endoscopes, they are small tubular telescopes that allow the physician to look inside joints and body cavities that otherwise could only be examined through a non-invasive procedure.
 |
| IMAGE OF RIGID TUBE |
A LENS OR LENS SYSTEM:
 |
| IMAGE OF LENS |
A lens to transmit the image of the patient’ internal system to the operator or viewer ( this is generally a relay lens in rigid endoscopes or multiple fibre-optics for fiberscopes), object lens allows visualization of mucosa.
A LIGHT TRANSMITTING SYSTEM:
A system to transmit light to enhance the visibility of the area of being examined ( the source of this light is usually based outside of the body, directed through optical fibres).
THE EYEPIECE:
 |
| IMAGE OF EYEPIECE |
An eyepiece in video scopes lacking eyepieces, images from inside the patient is sent to a screen for viewing and capture.
WATER PIPES:
 |
| IMAGE OF WATER PIPES |
The pipes serve to carry water which is used to wash the lens thereby maintaining a clear view.
THE OPERATIONAL CHANNEL:
 |
| IMAGE OF OPERATIONAL CHANNEL |
This is an opening of the device that is used to move various accessories to the distal end (of the endoscope) for surgery purpose, for example, biopsy channel this allows passage of biopsy forceps and other instruments to undertake therapy.
CONTROL CABLES:
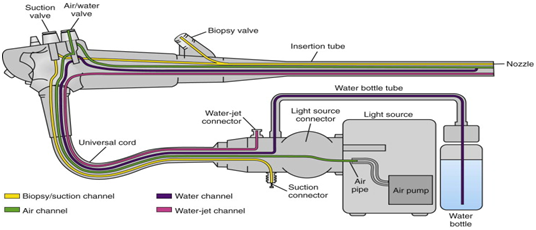 |
| IMAGE OF THE CONTROL CABLES |
This is used to control the direction
that the distilled end will bend as it moves through body cavities.
TOOLS USED WITH ENDOSCOPE:
An endoscope has a channel through
which the doctor can insert tools. These tools collect tissue or provide
treatment. Types of tools are:
- BIOPSY FORCEPS: These remove a tissue sample or a suspicious growth.











Since 1992, Darleys Surgical Co. has been recognized, globally, as a unique leader of innovation and design trends within the medical device industry. We have built an excellent reputation in the field by distributing a far-reaching range of surgical instruments and supplies that serve a variety of fields and disciplines.
ReplyDelete